
Antarctica's brief gain in ice mass fuels climate denial
- Published on June 2, 2025 at 19:02
- Updated on June 5, 2025 at 17:06
- 4 min read
- By Manon JACOB, Anna HOLLINGSWORTH, AFP USA, AFP Finland
"In a development that's leaving climate alarmists scrambling, new data shows that Antarctic ice has increased in size for the first time in decades -- reversing the long-touted trend of mass loss and environmental collapse," reads a May 28, 2025 Facebook post from The Hodgetwins, US conservative commentators whom AFP has previously fact-checked.

Similar narratives dismissing the impact of climate change popped up on social media after traditional media reported in early May on a study's findings about Antarctic ice sheet (archived here).
The study, from March, found that between 2021 and 2023, Antarctica's ice sheet expanded and therefore did not add to global mean sea level rise.
The gain did not, however, counter the overall rise observed over those years because of ice loss and warming elsewhere (archived here and here).
And weather conditions -- specifically unusual precipitations, including snow and some rain in east Antarctica and the Antarctic Peninsula -- were the primary reason the ice sheet gained mass, the study's corresponding author and other scientists told AFP.
This short-lived, partial gain does not disprove the impact of climate change on the continent, they said.
Short-lived reversal
Yunzhong Shen, the study's corresponding author, told AFP May 19 that the increase observed between 2021 and 2023 occurred on a "too short timescale" to be treated as a trend reversal -- or to deny the impacts of climate change in the region (archived here).
The gain witnessed in Antarctica's ice sheets also seems "to stop after 2024, which needs to be determined by further study," he said.
James Kirkham, a scientist with the International Cryosphere Climate Initiative scientist, concurred (archived here): "The most recent levels reported by NASA thus far in 2025 look similar to what they were back in 2020, just before the abrupt gain."
When looking at Antarctic total mass balance, NASA's dataset shows a net loss in mass since 2002.
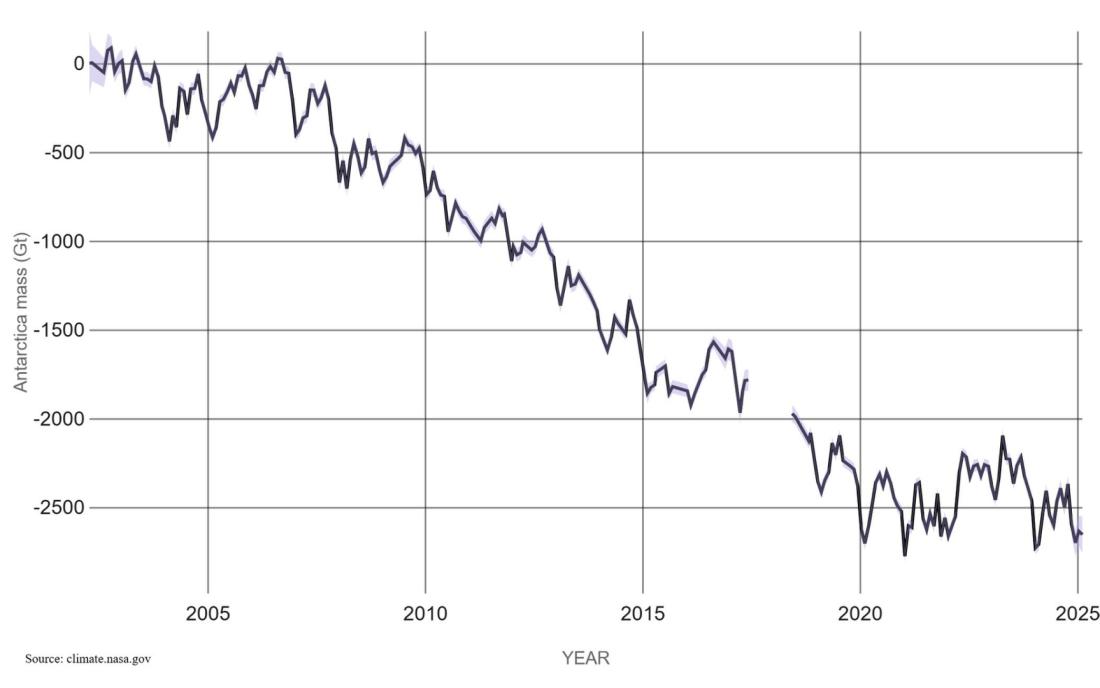
In fact, that "Antarctica would experience increased snowfall in a warmer climate is entirely expected as in a warmer climate the atmosphere can hold more moisture," Kirkham said in a May 27 email.
"This means that the likelihood of extreme weather (such as the heavy snowfall which caused the recent mass gain in east Antarctica) increases."
Brandon Daly, who studies glaciers and ice sheets, agreed (archived here).
"When climate change deniers talk about the glaciers in Antarctica, they will usually only focus on the surface of the ice sheet," he said May 28, explaining that they ignore other ice loss.
"Ice in contact with the ocean is what is melting, and it will continue to melt even if precipitation over the ice sheet increases," he said. "And it is the ocean-forced melting that is currently risking ice sheet instability and sea level rise."
Long trends observed
University of Minnesota climate scientist Peter Neff said May 27 that human climate change impacts in Antarctica are already widely seen around the Antarctic Peninsula and coastal Antarctica, but have been slower to penetrate inland (archived here).
The continent is "like a giant pancake with very steep edges that slow the north to south penetration of warmer air over the southern ocean," he said.
Almost all of Antarctica's ice losses come from glaciers, largely in west Antarctica and the peninsula (archived here and here).
Robert McKay, director of Victoria University of Wellington's Antarctic Research Centre, told AFP May 15 that scientists are mostly concerned with these sectors because they may be "near a tipping point" that could lead to greatly accelerated sea level rise (archived here).
Environmental change thus takes different forms in different regions.
Brief temporary offsets of overall losses through recent regional snowfalls, such as the one observed between 2021 and 2023, are unlikely to change the long-term trajectory of continent-wide ice losses, with continued warming.
Additionally, weather stations -- whose data network remains scarce in the continent -- have observed long-term warming and impacts on sea level rise, albeit with very large year-to-year variability given that Antarctica holds the most variable climate in the world (archived here and here).
Satellite data has recently revealed that ice sheets with enough frozen water to lift oceans some 65 metres are far more sensitive to climate change than previously suspected (archived here).
The amount of ice melting or breaking off into the ocean from Greenland and west Antarctica, now averaging about 400 billion tonnes a year, has quadrupled over the last three decades, eclipsing runoff from mountain glaciers.
Both polar oceans are warming, with the "Southern Ocean being disproportionately and increasingly important in global ocean heat increase," according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, the leading international consortium of climate scientists (archived here).
AFP has debunked other claims about the Poles, including here.
This article was updated to add metadata.June 5, 2025 This article was updated to add metadata.
Copyright © AFP 2017-2026. Any commercial use of this content requires a subscription. Click here to find out more.
Is there content that you would like AFP to fact-check? Get in touch.
Contact us




