Misleading posts about 'E. coli bacteria in Covid vaccines' spread online
- This article is more than two years old.
- Published on December 12, 2023 at 05:20
- 4 min read
- By Tommy WANG, AFP Hong Kong
"Understanding the role of E. coli in the production of mRNA vaccines," says a simplified Chinese post shared on October 11 on X, formerly Twitter.
"It can be hypothesized that the mRNA vaccines may contain E. coli toxins and DNA residues from the manufacturing process," it adds along with the hashtag "vaccine disaster".
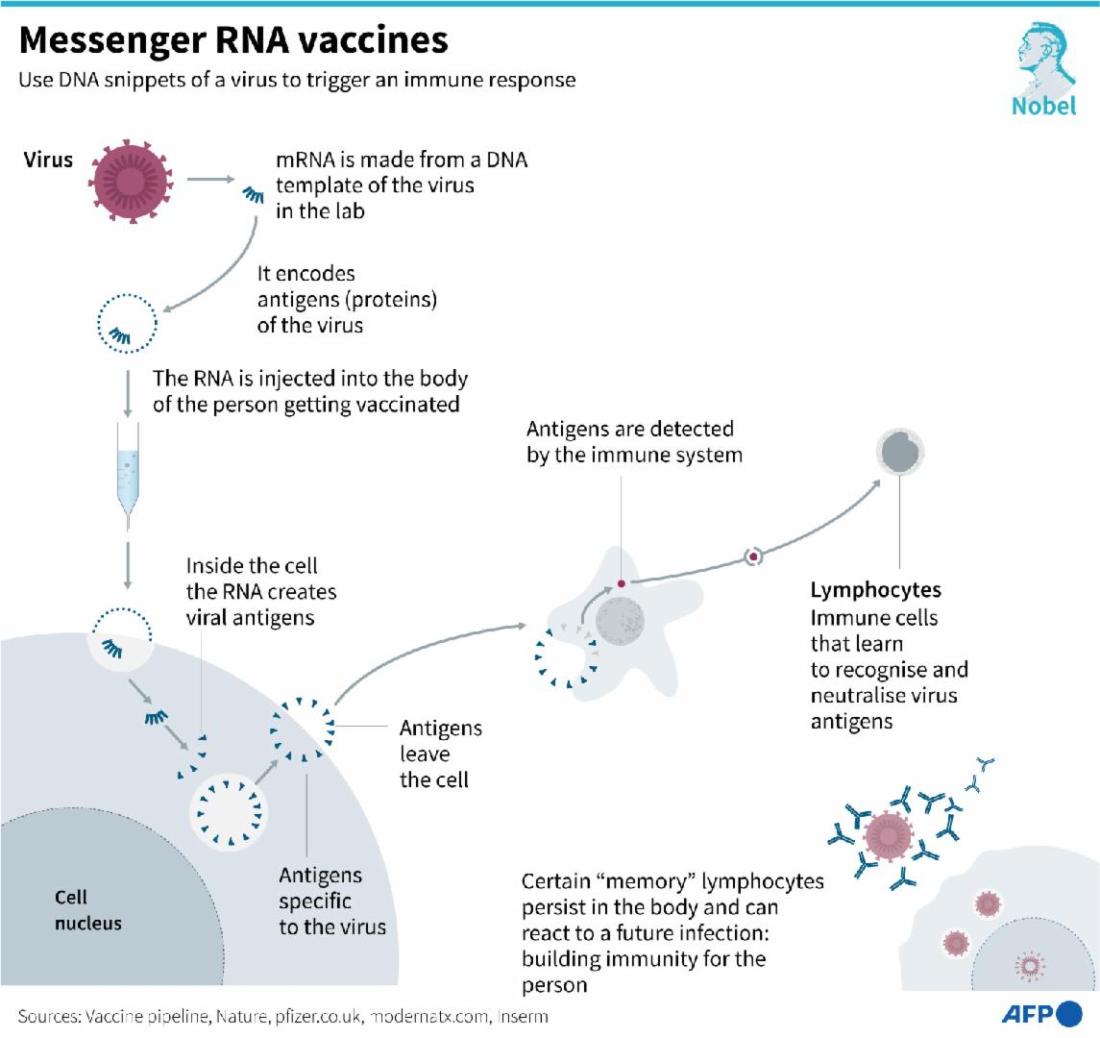
The post features a clip of a man, identified as Kevin McKernan, who says in part: "The way they manufacture these mRNA vaccines is they use a piece of DNA to xerox the RNA off."
He adds "lots" of DNA is needed to get the required amount of RNA for vaccines and one way to do this is through the use of E. coli bacteria.
"There's limitations on how much double-stranded DNA can be in products like vaccines. They are well above that by orders of magnitude from measurements."
The clip is part of a longer video earlier posted by Children's Health Defense, a group that has repeatedly published health misinformation.
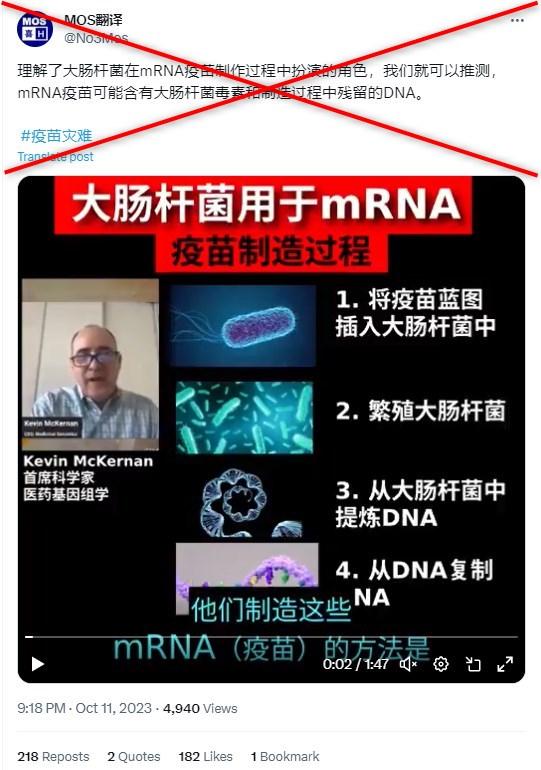
The claim has also been shared along with the same video on Facebook and Gettr.
Comments on the posts show many social media users believed the mRNA vaccines first approved for use against Covid-19 contain toxins.
"It's shocking that a vaccine with such unclear and potentially toxin-containing ingredients is still being forced on people!" one said.
"It's evil!" wrote another.
But multiple virologists separately told AFP while E. coli bacteria are used in vaccine development, these are "non-pathogenic" or does not cause disease.
'Harmless'
"E. coli used for biomedical applications are the non-pathogenic variants that don't produce toxins," Siddharth Sridhar, assistant professor of microbiology at the University of Hong Kong's Department of Microbiology, said on November 29 (archived link).
"No chance that pathogenic E. coli strains would contaminate mRNA vaccines."
Jesse Erasmus, director of virology at biopharmaceutical company HDT Bio, said the use of E.coli in making vaccines is "not new" (archived links here and here).
"A non-pathogenic, genetically modified form of E. coli is commonly used to produce DNA as well as proteins used in vaccines," he told AFP on November 4.
"For mRNA vaccines, E. coli is used to produce the DNA that is used to make the mRNA," he added.
E. coli -- short for Escherichia coli -- are a large and diverse group of bacteria found in the environment, foods, and intestines of people and animals.
Most strains are "harmless", according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention but some can make people sick and cause diseases such as diarrhoea, urinary tract infections, respiratory illness and pneumonia (archived link).
'Vigorous' safety tests
Moreover, Erasmus said that mRNA vaccines "go through a vigorous set of assays before they can be released for use in humans".
Amira Roess from George Mason University's College of Public Health separately said "multiple steps" are in place to ensure vaccines are free from contaminants.
"After the E coli is killed and the part that we need to make the vaccine is removed, there are multiple steps in the process to ensure that no contaminants from E coli make it into the mRNA vaccine," Roess told AFP in an email on November 9.
"All of this makes me feel confident that the mRNA vaccine delivered into my arm is free from contaminants that can cause E. coli infection."
DNA fragments
AFP has repeatedly debunked claims that Covid-19 vaccines contain DNA, alter people's genomes and cause cancer.
"There are limits for the amount of DNA that can be in a vaccine so if contamination is present it will be quality control checked to be below that limit," Amesh A. Adalja from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health told AFP on December 5 (archived link).
"There is no evidence that the DNA contamination -- if present -- would be harmful to humans."
The misleading posts are "attempting to draw attention away from the established safety data and have people focus on things that sound scary", Erasmus said.
Health Canada previously said: "The mRNA never enters the central part (nucleus) of the cell, which is where our DNA (genetic material) is found, and the cells' DNA cannot be altered by mRNA vaccines."
While the ingredients list for mRNA Covid-19 vaccines do not mention DNA, University of Michigan virologist Michael Imperiale previously said he "can't think of anything dangerous" that would happen if they did.
To affect a person's genome, he said contaminants would need to enter "dividing cells" -- not the muscle or skin cells where the vaccine is introduced.
Data gathered from global inoculation campaigns show Covid-19 vaccines are safe.
While serious side effects are possible, these cases are "extremely rare" according to the World Health Organization (archived link).
Medical professionals have consistently said the benefits of receiving Covid-19 jabs outweigh the risks of adverse reactions.
Copyright © AFP 2017-2026. Any commercial use of this content requires a subscription. Click here to find out more.
Is there content that you would like AFP to fact-check? Get in touch.
Contact us