Consuming cold drinks after eating mangoes does not 'cause death’: experts
- This article is more than two years old.
- Published on May 11, 2023 at 11:29
- 1 min read
- By Mohammad MAZED, AFP Bangladesh
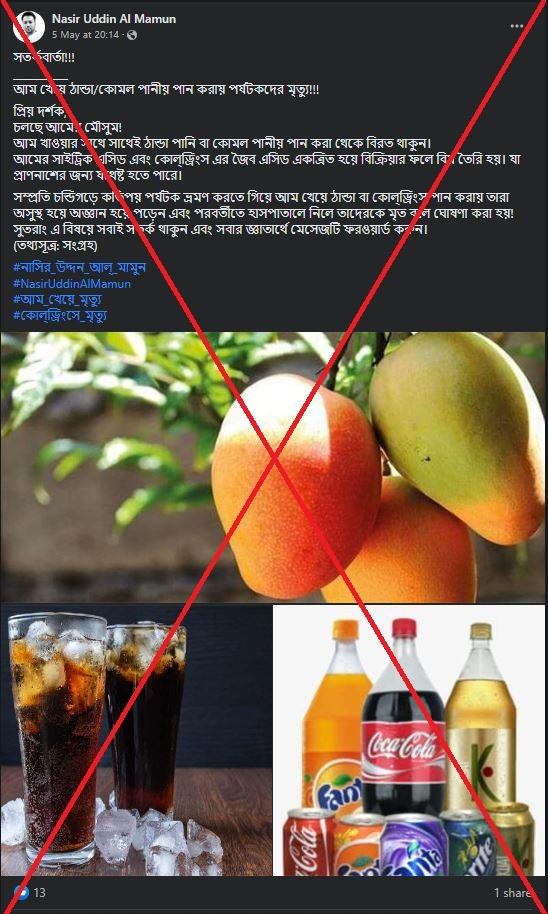
The claim was shared on Facebook here on May 5, 2023.
The Bengali-language caption translates to English as: “WARNING!!! Tourists die after eating mangoes and drinking cold/soft drinks!!!
"Dear visitor, Mango season is underway! Avoid drinking cold or soft drinks immediately after eating mangoes. The citric acid of a mango and the organic acid of cold drinks combine to form a poison. Which can be enough to cause death."
The post goes on to refer to an alleged case in the northern Indian city of Chandigarh, saying: "Recently some tourists while traveling in Chandigarh fell sick and fainted after eating mangoes and drinking cold drinks and were later declared dead in the hospital!”
The same false claim was shared here and here on Facebook.
AFP could not find any official reports of deaths following the consumption of cold drinks and mangoes in Chandigarh.
Public health experts told AFP that the posts were false.
Dr Taufique Joarder, the vice chairperson of the Public Health Foundation of Bangladesh, said the claim was "baseless".
"There is no reason to lose lives for drinking cold drinks after eating mangoes unless there is anything poisonous in any of the items," he said.
Nazma Shaheen, professor at the Institute of Nutrition and Food Science of Dhaka University, told AFP there was no substantial evidence that a person will suffer a dangerous reaction if they mix mangoes and cold drinks.
"I think some people are deliberately sharing this information to mislead people," she said.
Rumi Ahmed, associate professor at the Dell Medical School of the University of Texas at Austin, also said the claim was "completely false.”
Copyright © AFP 2017-2026. Any commercial use of this content requires a subscription. Click here to find out more.
Is there content that you would like AFP to fact-check? Get in touch.
Contact us
